Gas prices are soaring to record highs, and as such electric cars are becoming ever more popular.
And why not? EVs are far cheaper to run, provide terrific performance, and, with the amount of public rapid chargers expanding across the country, it’s easier (and faster) to charge one than ever. Batteries are also getting bigger, so an EV can travel farther on a single charge.
But, are electric cars better for the environment? They obviously spew no emissions, but there’s no doubt that at least some of the electricity you use to charge an electric car comes from fossil fuels. Not to mention the environmental cost of actually building one.
And as someone who recently bought a new electric car, beyond the savings I’m seeing, it’s an important question I want answered too. Here’s what I found.
Never miss an amazing deal again + get our bonus 250+ page eBook for FREE. Join 50,000 other Canadians who receive our weekly newsletter – learn more.
Overview of gas vs. electric car environmental impact
Here’s an overview of the environmental impact of electric and gas cars.
We’re only looking at pure electric cars – our discussion doesn’t include hybrids or plug-in hybrids that use a mixture of electricity and gas to run a vehicle.
Here’s a quick comparison of these 2 types of cars.
| Feature | Electric Car | Gas Car |
|---|---|---|
| Tailpipe emissions | No | Yes |
| Maintenance costs | Only requires annual checks | Frequent oil changes, other annual maintenance requirements |
| Electricity/fuel efficiency (mid-size car) | 18 kwh/100 km | 7.5 L/100 km |
| Price per kWh, L | $0.14 | $1.70 |
| Cost to drive 1,000 km | $25.20 | $127.50 |
| Typical range on a single charge/fillup | 400 km | 800 km |
Electric cars have some significant advantages. Not producing any emissions is obviously a big plus.
But there are plenty of cost savings. Let’s start with maintenance. An electric car generally only needs an annual checkup, and not much has to be done to it. Basically, all it takes is a look over, and giving the brakes a cleaning.
That’s not the case for a gas car that needs regular oil changes, annual checks, on top of all the other maintenance a gas car needs.
But more than that – the main advantage is the straight cost just to get around. The electricity you pay for an EV is far cheaper than the gas required to power an equivalent car.
Based on our numbers above, it’s around 80% cheaper to run an electric car over an equivalent gas car. With my electric car, I find I’m saving around $340 a month over the car I previously replaced, which is driven 3,000 km per month.
But all these advantages come at a cost. EVs have a shorter range than a gas car. Filling up a gas car is also much quicker, and gas stations are plentiful.
With EVs, how fast you can charge your car depends on your car’s charging capabilities, as well as the charger you’re using. It can take as little as 20 minutes, but could also be as much as an hour or more.
With that said, most of your charging would be at home, where you can just let it charge overnight while you’re sleeping. But if you need a quick charge because you’re travelling, you have to plan in advance.
How electric cars help the environment
This section will talk about the ways electric cars are environmentally better than gas cars.
Tailpipe emissions
A big benefit of an EV car is they don’t produce tailpipe emissions. For large urban areas that deal with poor air quality (hello Toronto), electric cars can help by not producing any emissions whatsoever.
And breathing cleaner air is good for everyone.
Maintenance costs
The maintenance costs are considerably less with an EV than a gas car.
Why? It’s all in the number of moving parts. A typical gas car has around 2,000 moving parts.
But an EV? A mere 20. And it goes without saying, it’s much easier to maintain a vehicle with far fewer moving parts.
In fact, an EV generally only requires one check per year and most of it has to do with checking the brakes. Plus, thanks to regenerative braking on EV cars, you’ll have to replace those parts far less than you would for a gas car.
But a conventional gas car needs much more than that, namely in the form of oil changes. But there are more maintenance costs, like transmissions, exhaust, and radiators.
How much can you save? Consumer Reports expects that over the life of a vehicle, you would save around $4,600 on maintenance with an EV. And that’s based on older generation EVs.
With that said, one big issue to consider with an electric car is the batteries. At some point in time, the battery will need to be replaced, and that’s a big job.
But modern batteries can now last for 10 years before that’s something you may need to consider. How many people actually hold onto a car for that long?
How does this help the environment? You’re cutting out a lot of oils and fluids that need to be produced and recycled. Not to mention the energy savings associated with getting someone to look over your vehicle only once per year.
3 environmental issues with electric cars
Electric cars aren’t perfect, there are still environmental issues with them.
The electricity generated probably contains at least some level of fossil fuel burning and there’s also the manufacturing process to consider. Quite a few materials are needed to produce the lithium-ion batteries on electric cars.
And at the end of the day, when the car is no longer being used, there’s the disposal of the battery to contend with.
Here’s a closer look at these 3 issues.
EV battery production process
EVs consume more energy to manufacture and that’s largely from the batteries.
Lithium ion batteries are manufactured from a blend of rare materials and it takes a good amount of energy to both extract them and turn them into the final product needed to actually make the battery.
But more than that, it also matters where the battery is made. If your battery is made in China, it generates 66% more emissions than a battery made in Europe or North America.
If manufactured properly, an EV car doesn’t really have more emissions than an internal combustion engine.
And EV battery plants are coming here. Just recently, it was announced a plant will be built in Windsor.
In short, building an EV car may bring more emissions in the short-term, but they are likely to decline over the long-term.
Electricity sources
The next big question when it comes to emissions and electric cars – how is your energy produced?
We’re not at a stage where all of our power comes from green energy. There’s undoubtedly some mix of fossil fuels being used to produce electricity in Canada.
But unless the vast majority of your electricity is being generated by coal, EVs still are better for the environment.
And here in Canada, that vast majority of our electricity is generated from clean sources.
The following will obviously vary by province, but here is a percentage breakdown of where our power comes from (numbers are from the government of Canada from 2018).
| Percentage of emissions | |
|---|---|
| Coal | 8% |
| Natural Gas | 9% |
| Hydropower (hydro dams/tidal) | 61% |
| Biomass, Geothermal | 1% |
| Wind | 5% |
| Nuclear | 15% |
| Others (oil, solar) | 1% |
Only 18% of Canadian power as of 2018 was generating CO2 emissions. Here’s how it looks for the visual learner.
Lots of our electricity comes from various forms of hydropower, followed up by nuclear and wind energy.
Want to see where it is produced in Canada? Here’s a map showing the various types of power generation, the type, and how much power is being created.
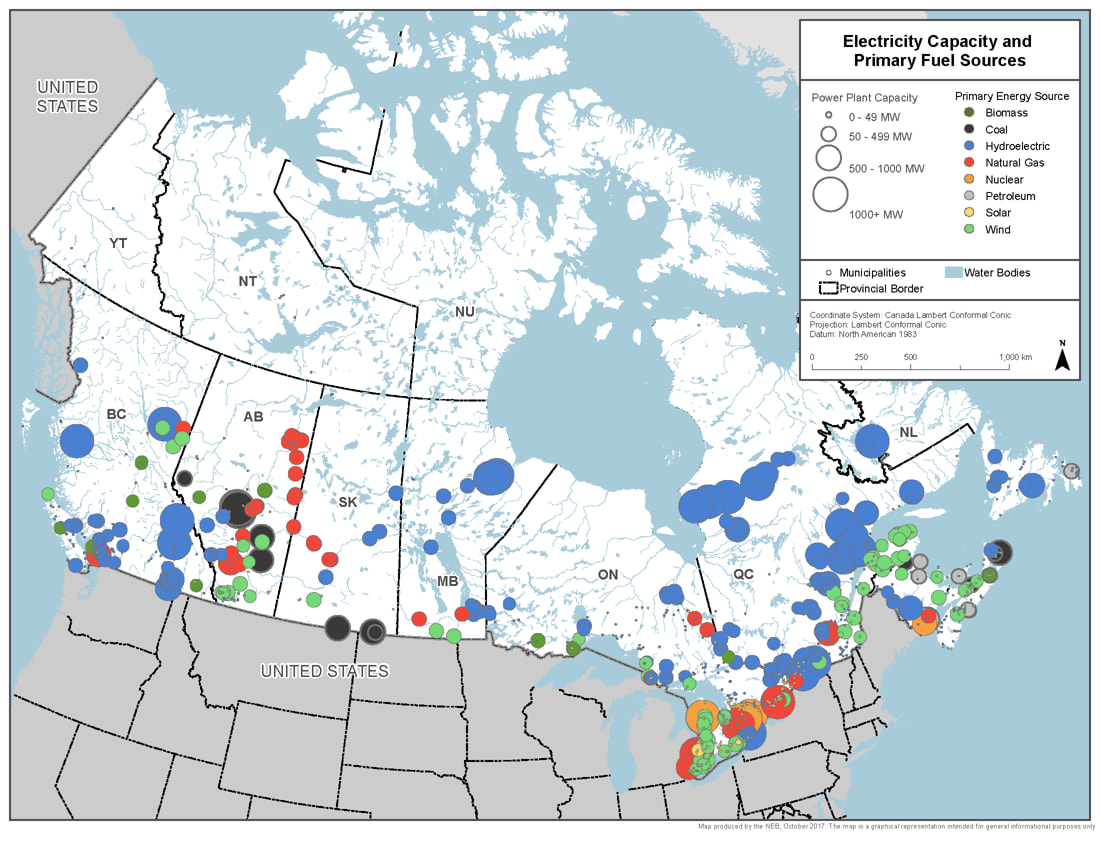
Source: Canada Energy Regulator
There’s one important point to note about gas powered cars – only 30% of the gas you burn actually goes into powering the car, the rest is simply generating heat or other efficiency losses. With your EV, almost all the electricity you’re using is going to power your car, save for heaters, lights, and other accessories.
EV battery end of life
This is one issue that needs resolving – what to do with the batteries once they need to be replaced, or the car is heading off to be turned into scrap.
Regular car lead-acid batteries are one of the most recycled products in the world.
But lithium ion batteries are a different beast, and they’re not as easy to recycle. To be clear, they do get recycled, but with the standard recycling method, some of the materials needed to make new ones can’t currently be recycled and new material needs to be mined.
They can be fully recycled, but it’s an intensive process that costs a lot of money, and it’s cheaper to mine new lithium instead.
But there is more positive news, as the number of EV batteries grows, better solutions will come around, and make full recycling of EV batteries more economical.
Cost of electric cars vs. gas cars
We’ve determined that electric cars are better than the environment and are cheaper to run.
But they also cost more. How much? One easy way to find out is by looking at cars that have the option of running on gas or being pure electric.
One such option is the Hyundai Kona.
Looking at the preferred version (the electric version isn’t available in the base trim), and not including any taxes, delivery fees, or any extras, here’s what the car costs if you get one with a gas engine or is all electric:
- $26,055 for gas
- $45,851 for electric
Eep. That’s quite a bit more to pay for an electric car and one reason adoption of them is slow.
To make up for that extra cost, you will have to drive quite a bit to offset it.
But, there are programs to lower the cost of a new EV.
Keep in mind the federal and provincial incentives
There are federal and provincial programs available that will rebate the cost of an electric car.
The federal government runs a rebate program on new electric cars. As long as the base level trim of an electric car is less than $46,000, you can get $5,000 off your new electric car.
Many provinces also run their own rebate programs you can check out. This CAA site has a quick rundown on what provincial rebates are available. Depending on the province, you can get up to $8,000 and a free charger.
They won’t offset the entire cost, but can make a substantial difference in the amount you pay.
Want a chance at a free Tesla?
Want a free electric car? We’re running our own promotion to win a Tesla Model 3.
Simply get approved for a credit card through our GeniusCash program and you’ll be entered in a draw to win either $10,000 or a Tesla Model 3.
Want to learn more about our Tesla giveaway? Here’s how it works.
Conclusion
There isn’t a mode of travel that’s perfect for the environment. But with an electric car, you can reduce your carbon footprint and save money while you’re driving it.
And of course, there’s always our Tesla giveaway to give you a chance to get an electric car for free.
Do you have an electric car? How has your experience been with it to date?
Let us know in the comments below.
FAQ
Are electric cars better for the environment than gasoline cars?
Unless the majority of your electricity comes from coal power plants, electric cars are much better for the environment, as they expend fewer emissions while in operation.
What part of the electric car manufacturing process is the most damaging for the environment?
Producing the lithium ion battery causes the most damage to the environment. Several materials need to be mined to make them and it can take quite a bit of energy to actually produce the battery used in an EV.
Is now the best time to buy an electric car?
With ample government rebates, it’s not a terrible time to buy an electric car. However, they aren’t produced as much as gas cars and you may end up waiting a while before actually receiving one.
creditcardGenius is the only tool that compares 126+ features of 228 Canadian credit cards using math-based ratings and rankings that respond to your needs, instantly. Take our quiz and see which of Canada's 228 cards is for you.








 GC:
GC: 






























Comments
Leave a comment
Required fields are marked with *. Your email address will not be published.
Showing 9 comments